“Hot cross bun” sign in a patient with parkinsonism secondary to presumed vasculitis Journal
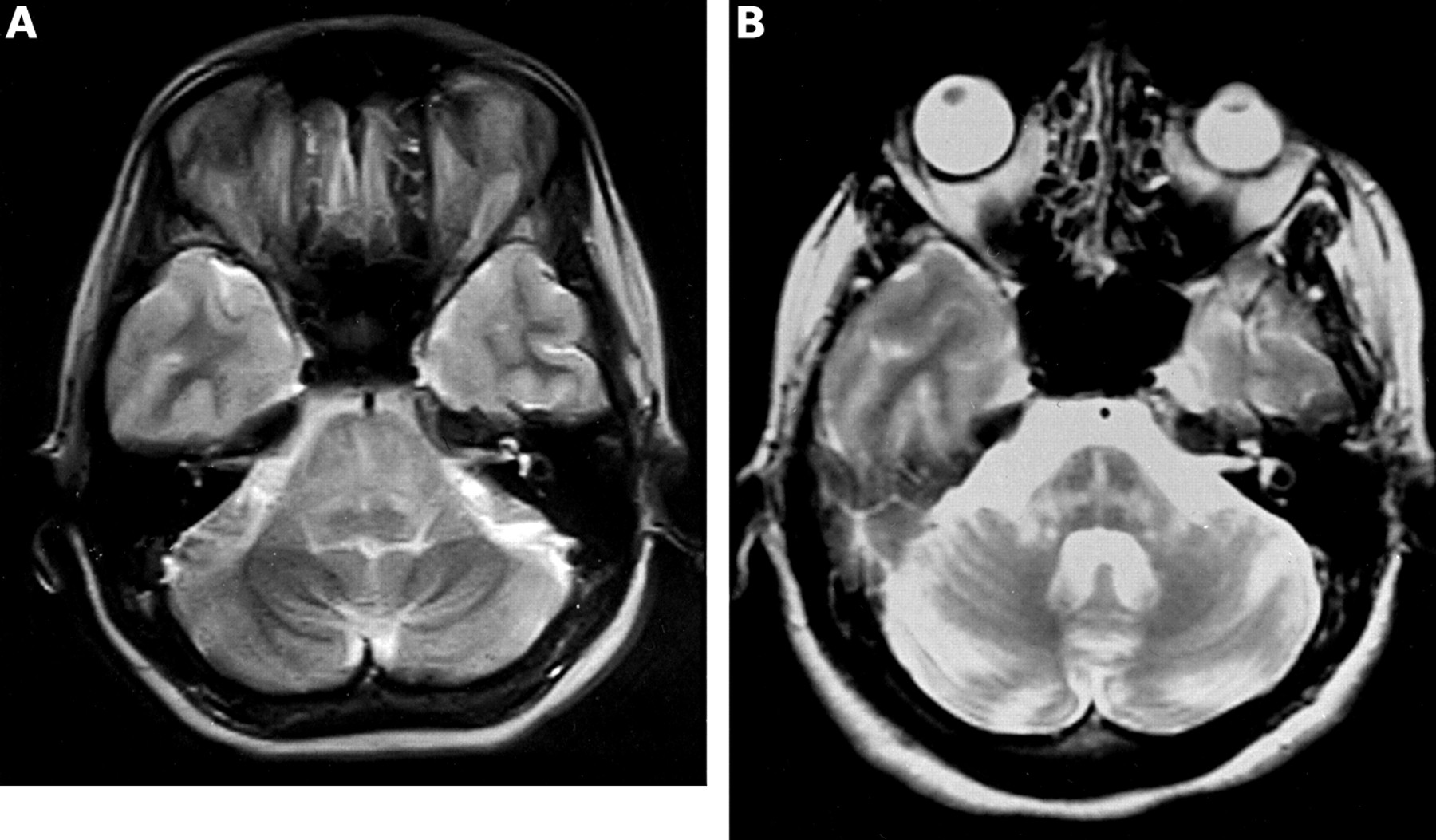
The "hot cross bun" sign is characterized by cross-shaped T2 signal hyperintensity within the pons and has been said to be specific although not pathognomonic for multiple system atrophy (MSA). 1 Case 1 is a 60-year-old woman who presented with progressive spasticity, limb ataxia, and urinary incontinence of 3 Undefined control sequence \ ( Unde.

“Hot cross bun” sign in two patients with multiple system atrophycerebellar Neurology
FIG. 1 (A) Figure demonstrating the hot cross bun sign in a patient with MSA‐C; (B) evolution of the etiologies associated with the hot cross bun sign. A majority of the new conditions associated with the HCB are rare and have been described only in a few case reports.
(PDF) The hot cross bun sign
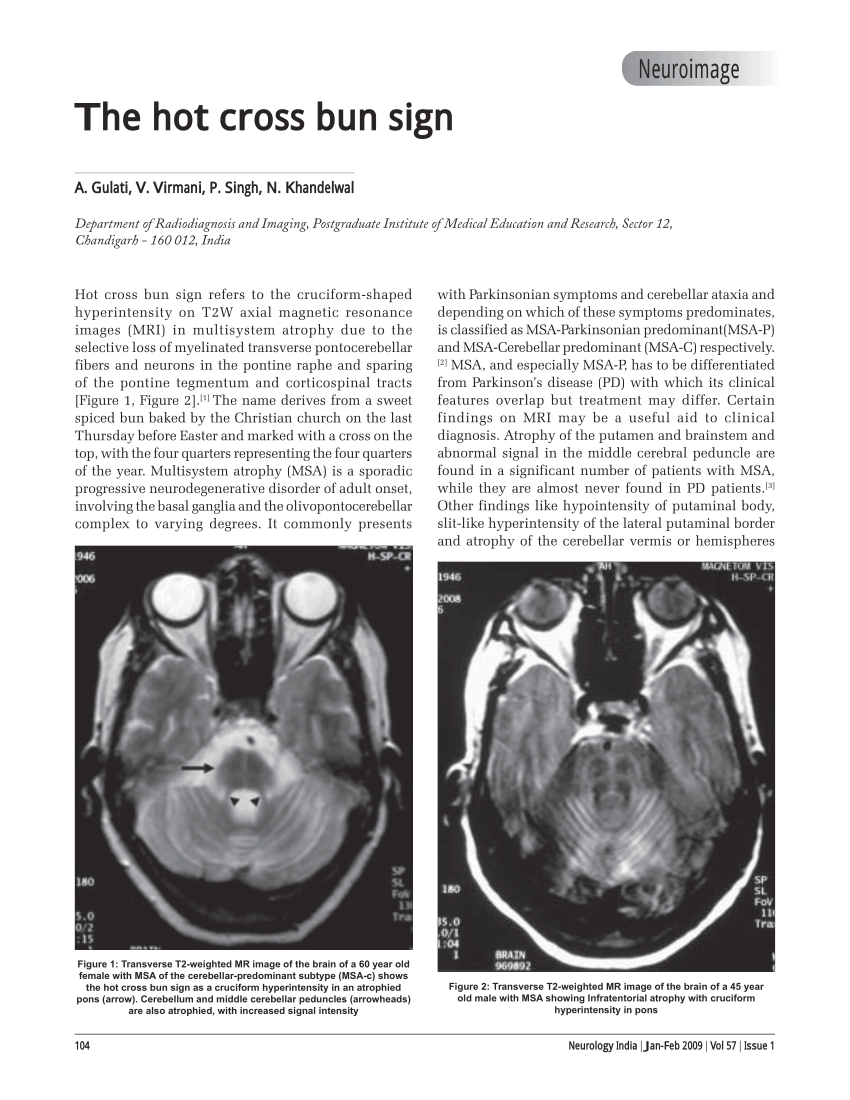
The hot cross bun sign refers to the MRI appearance of the pons when T2 hyperintensity forms a cross on axial images, representing selective degeneration of transverse pontocerebellar tracts and median pontine raphe nuclei 1. It has been described in a variety of neurodegenerative and other conditions. Common associations include:
hot cross bun sign The Scribble Doctor
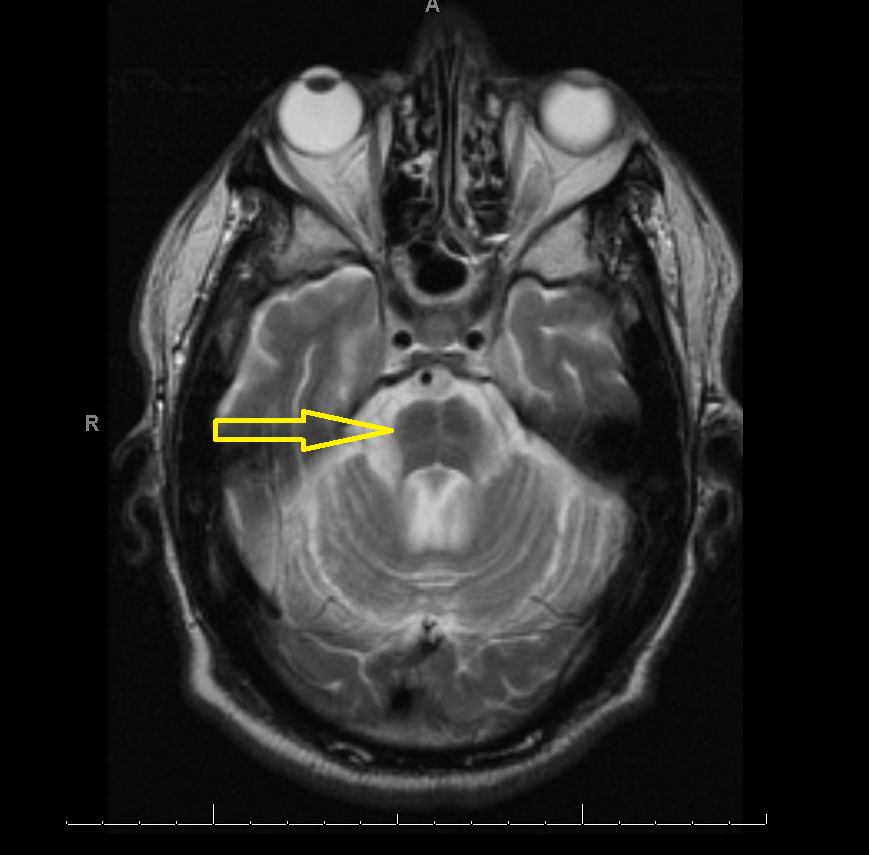
Hot cross bun sign is seen in the pons in a Multiple system atrophy (MSA) patient, the sign has also seen with other neurodegenerative diseases such as spinocerebellar atrophy and parkinsonism. In appropriate clinical setting, detection of these changes is useful to confirm the diagnosis of MSA. Related Radiopaedia articles

Hot Cross Buns Yard Sign by trendyteeshirts
The "hot cross bun" (HCB) sign refers to a cruciform-shaped hyperintensity within the pons found on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This is a rare MR finding, and it is most commonly associated with atrophy of the pons, cerebellum, and putamen in cerebellar variant multiple system atrophy (MSA-C).
Radiodiagnosis Imaging is AmazingInteresting cases Hot cross bun sign Multiple system atrophy
The "hot cross bun" sign (HCBS) at pons and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) are helpful. However, the prevalence of HCBS and the alteration of cerebellar MRS parameters are evolving with.

Hot Cross Bun Sign. Head T2W MRI though the pons showing a hyperintense... Download Scientific
The Hot Cross Bun Sign: A Journey Across Etiologies. The Hot Cross Bun Sign: A Journey Across Etiologies Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2022 Oct 21;9(8):1018-1020. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.13596. eCollection 2022 Nov. Authors Shweta Prasad 1 , Malco Rossi 2 3 Affiliations 1 Department of.

Axial T2weighted MR image of the brain showed the 'hot cross bun sign'... Download Scientific
Changes are mostly infratentorial, 4 and include the typical hyperintense hot cross bun sign in the pons and other anomalies, such as putamen atrophy, putamen hypointensity and hyperintense putaminal rim. 2-5 The hot cross bun sign is the result of the degeneration of pontine neurons and transverse pontocerebellar fibres.

Figure 1 from The hot cross bun sign. Semantic Scholar
The "hot cross bun" (HCB) sign, a cruciform hyperintensity in the pons on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has gradually been identified as a typical finding in multiple system atrophy, cerebellar-type (MSA-C).

Hotcross bun sign of multiple system atrophy Image
The "hot cross bun" sign is a cruciform hyperintensity is seen on T2 weighted imaging within the pons. The sign is considered to be pathognomic for Multiple system atrophy type C. The clinical and radiological features of Multiple system atrophy type C overlap with the autosomal dominant inherited ataxias. We present a case series of 3.

Hotcross bun sign in multiple system atrophy Eurorad
The hot cross bun" sign is characterized by cruciform T2 signal hyperintensity within the pons and has been said to be specific although not pathognomonic for multiple system atrophy (MSA). Pontocerebellar degeneration results in lateral as well as longitudinal pontine fibers becoming evident as high signal on T2, manifesting as "hot cross bun.
Radiodiagnosis Imaging is AmazingInteresting cases Hot cross bun sign Multiple system atrophy
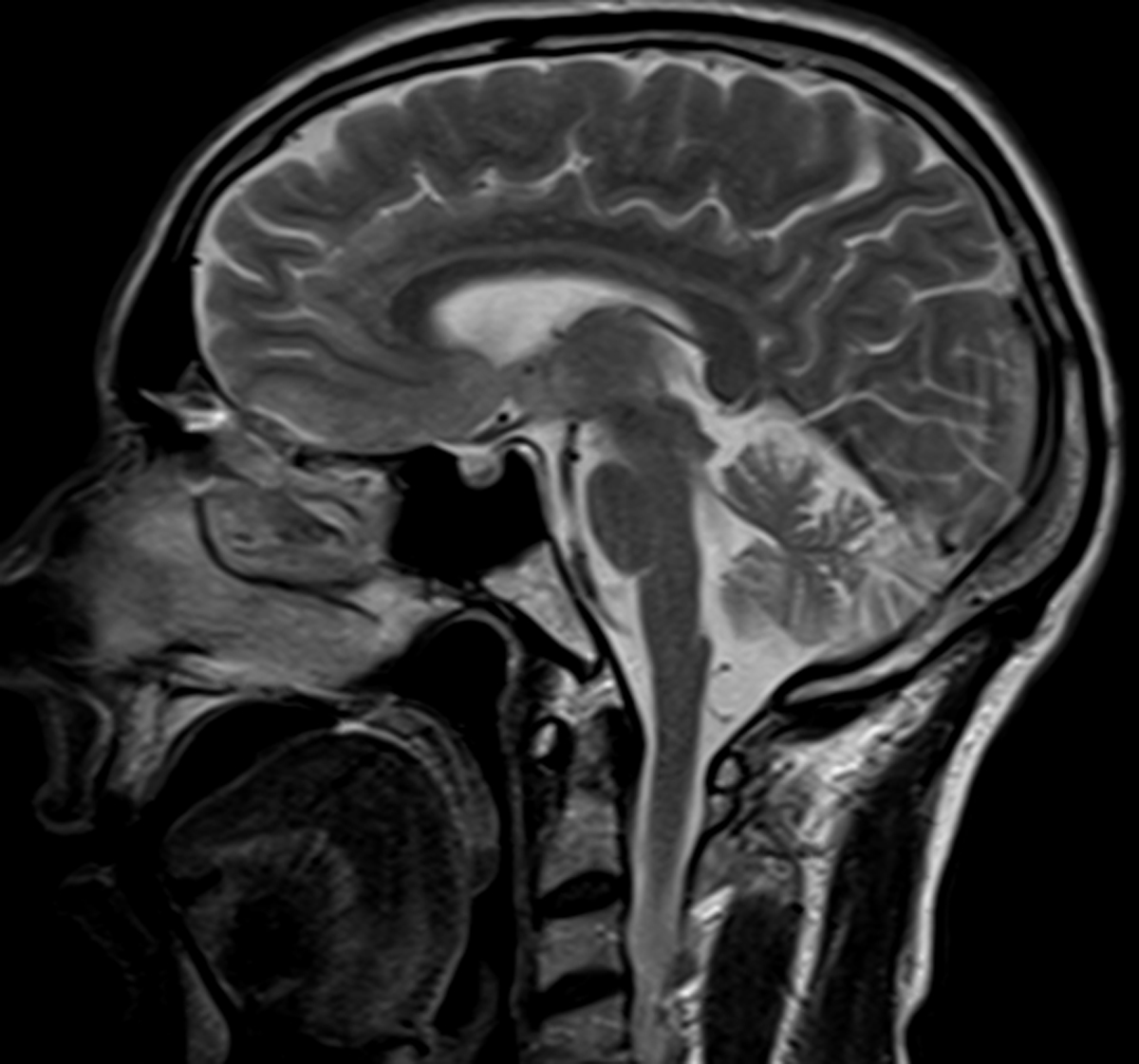
The "hot cross bun" sign refers to pontine cruciform hyperintensity on long TR sequences, which can be observed in multiple-system atrophy, spinocerebellar atrophy types 2 and 3, 1 and in parkinsonism secondary to vasculitis. 2 It has not been previously demonstrated in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), to our knowledge.

“Hot cross bun” sign in two patients with multiple system atrophycerebellar Neurology
Conventional magnetic resonance imaging is frequently used in the diagnosis of MSA, and "hot cross bun" sign (HCBs) is widely accepted to be a valuable sign for the diagnosis of MSA 6,7,8,9,10.

(PDF) Hot Cross Bun sign associated with SCA1
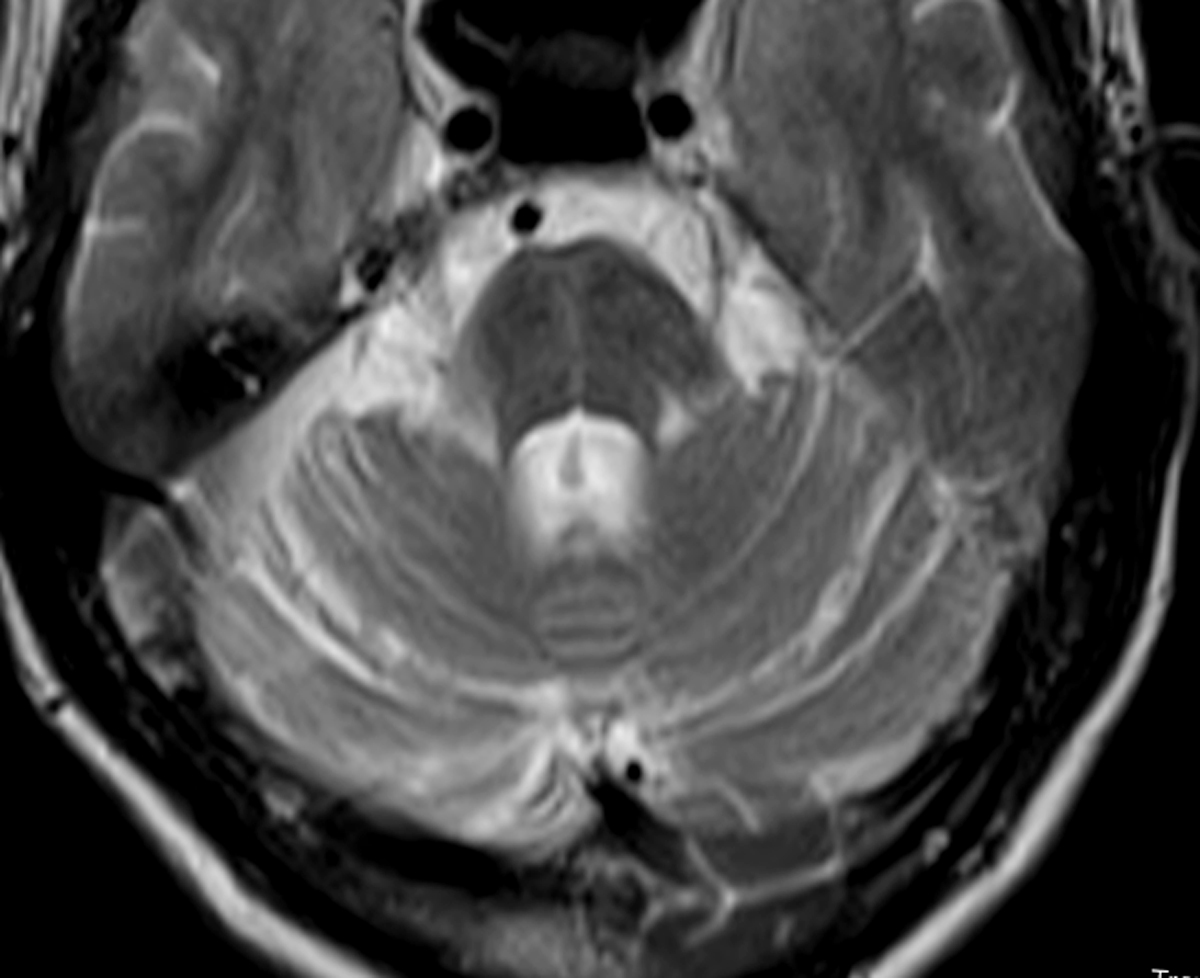
The 'hot cross bun' sign (HCBS) is a radiologic finding describing a cruciform T2 hyperintense signal on axial MRI of the pons.
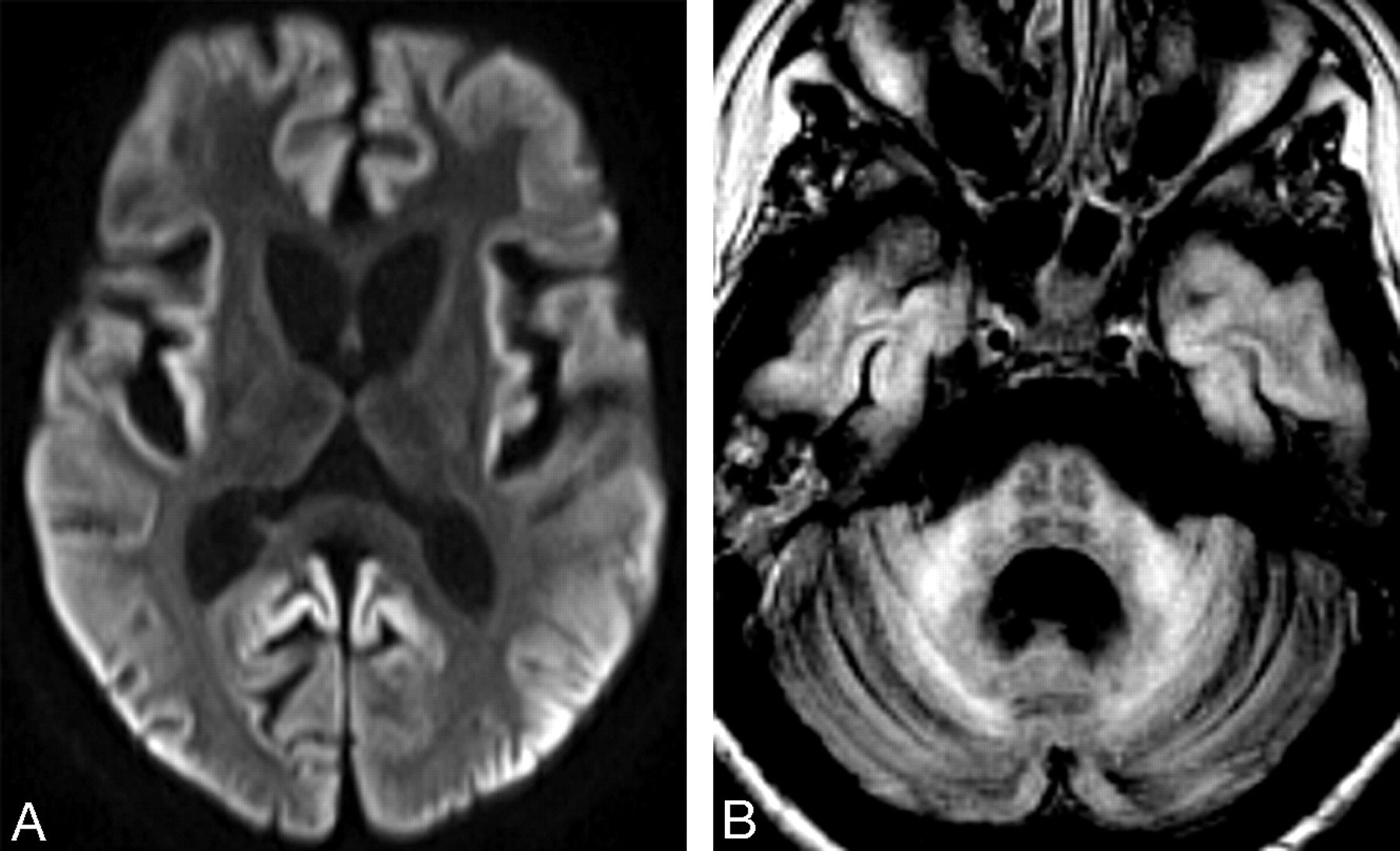
“Hot Cross Bun” Sign in Variant CreutzfeldtJakob Disease American Journal of Neuroradiology
The "hot cross bun sign" (HCBs) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been initially considered specific for multiple system atrophy with cerebellar features. However, a number of other conditions have since been described, which may be associated with this imaging sign.

Hot Cross Buns Posters Redbubble
Brain MRI disclosed the "hot cross bun" sign typical of multiple system atrophy (MSA) ( figure ). 1,2 This sign is probably related to degeneration of transverse pontocerebellar fibers, whereas the hyperintense rim bordering the putamina has been associated with neuronal loss, reactive microgliosis, and astrogliosis. 2 Glial cytoplasmic inclusio.